Leen Helmink Antique Maps & Atlases
www.helmink.com
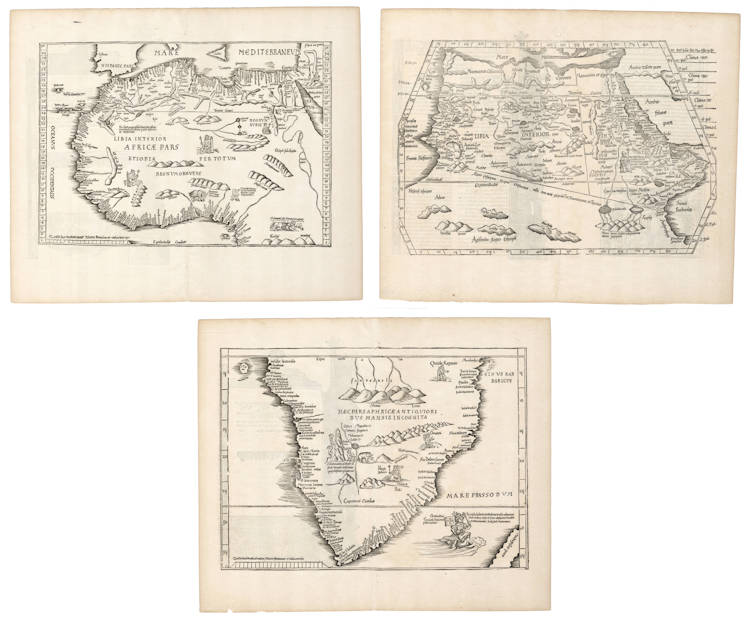
Fries / Waldseemüller / Ptolemy - Tabula Moderna Primae partis Africae, Tabula Moderna Secundae partis Africae, Tabula III Aphricae
Certificate of Authentication
This is to certify that the item illustrated and described below is a genuine and
original antique map or print that was published on or near the given date.
Dr Leendert Helmink, Ph.D.
Cartographer
Laurent Fries
First Published
Strassburg, 1522
This edition
1525 second edition
Size
each ca 27.7 x 40.3 cms
Technique
Woodcut
Stock number
19076
Condition
pristine
Description
Enter Vasco da Gama
Uniform set of three extremely early explorer maps that present the Portuguese exploration and discovery of the sea route to the Indies. The maps are icons from the age of exploration.
From the rare 1525 Strassburg edition. The woodcut decorations on the back are attributed to Albrecht Dürer, who also made the woodcut of the armillary sphere in this atlas.
Like many maps in Fries' atlas, cartographically these maps are slightly reduced versions of corresponding maps in Martin Waldseemüller's atlas of 1513. But while the Waldseemuller are spartan in nature, Laurent Fries has added fascinating text legends and decorations that come from Waldseemüller's 1516 updated wall map of the world that had been published in the meantime. Of special interest is the image of Portugal's King Manuel riding a sea monster near the southern tip of Africa. His control of the sea monster expresses Portugal’s confidence in navigating the ocean, as well as Portugal’s mastery of the sea route to India around the Cape of Good Hope, pioneered by Vasco da Gama.
Condition
Uniform set. Strong early impressions of the woodblocks. Thick and clean paper. Minimal shine through of the verso text and woodcuts as always. Ample margins all around. No restorations or imperfections. Exceptional look and feel. Pristine collector's condition of three uniform items from the dawn of the charting of the earth.
The corresponding 1513 Waldseemüller versions of these maps
Tabula Moderna Prime Partis Aphricae
Tabula Moderna Secunde Porciones Aphrice
Tabula Quarta Africae
Nordensjköld on the 1513 progenitors
The most important maps in the Ptolemy of 1513, however, are the two maps of Africa in double-folio which I have reproduced here. They form admirable though hitherto completely neglected illustrations of one of the most important episodes in the history of Navigation, and they are evidently directly based on carefully registered observations during the Portuguese exploring voyages round Africa to India.
For their exactness, and in the richness of names along the coasts of Africa, these maps are comparable with the old portolanos of the Mediterranean Sea.
The corresponding map of Asia [as well as the Fries version of it] shows on the contrary that the geographical notions about the Indian Peninsulas when the map was drawn (1507?) were still very vague in Europe, and dependent on hearsay.
(Nordenskjöld)
Map 1: First modern map of Africa north of the equator.
"This map is [a reduced version of the map] from Waldseemüller's Ptolemy atlas of 1513. As northern Africa was better known than southern Africa at that period it has more geographical information, especially in the interior. Various kingdoms are described, with a multitude of coastal names, and as with the southern part these are placed within the coastline. The Mediterranean and Red Sea are prominently featured as well as a number of islands on the northwest coast - Madeira, the Canaries, etc. - which at that time were already well known to the Portuguese in their initial efforts to discover a route to the Indies."
(Norwich on the 1513 version).
"Prior to 1513 any printed maps showing the North African coastline had been based on the ancient Ptolemaic geography. Here, Waldseemüller has made use of Portuguese reports to give more detail and a better outline than before for the western coasts. During the previous century the Portuguese, under Prince Henry, had gradually travelled further south - Cape Bojador, just south of the Tropic of Cancer, had been passed in 1434; Cape Verde was reached in 1444; and, after a halt in voyages, by 1481 the Equator had been traversed; only seven years later, Dias rounded the Cape."
(Potter on the 1513 version).
Map 2: First modern map of Africa south of the equator.
"This fine woodcut map of South Africa depicts the area from the equator to the Cape of Good Hope, together with most of Madagascar. The coastline is full of names of rivers and bays, printed inland from the coast, using many of Portuguese origin. The prominent central mountain range is called Mons Lune and described as the origin of the Nile."
(Norwich on the 1513 version).
"This reissued map [after Waldseemüller 1513] now has three kings on their thrones, an elephant, a cockatrice and two serpents next to a sugarloaf mountain, while the king of Portugal rides a bridled sea monster on the Mare Prassodum, holding the banner of Portugal in his right hand and the sceptre in his left. Mountains are added and inland rivers appear to the south of the Mountains of the Moon."
(Norwich).
"A fascinating reissue of Waldseemüller's map - the first of South Africa."
(Potter).
Map 3: Ptolemy's overview map of Africa.
To complete the set of modern maps that reveal the latest Portuguese explorations and the new found gateway into the Indian Ocean, the Ptolemaic overview map of Africa gives Ptolemy's refuted view of Africa attached to the southland and a landlocked Indian Ocean.
Fries map is a reduced version of the Waldseemuller 1513 Ptolemaic overview map of Africa.
The text legends on the maps
For detailed transcriptions and translations of the Latin text legends on this map, as well as the sources for them, please do not hesitate to ask us.
Laurent Fries (c.1490-c.1532)
Laurent Fries (Laurentius Frisius), born in Mulhouse in Burgundy, travelled widely, studying as a physician and mathematician in Vienne, Padua, Montpellier and Colmar before settling in Strassburg. There he is first heard of working as a draughtsman on Peter Apian's highly decorative cordiform World Map, published in 1520. Apian’s map was based on Waldseemüller's map of 1507 which no doubt inspired Fries's interest in the Waldseemüller Ptolemy atlases of 1513 and 1520 and brought him into contact with the publisher, Johannes Grüninger. It is thought that Grüninger had acquired the woodcuts of the 1520 edition with the intention of producing a new version to be edited by Fries. Under his direction the maps were redrawn and although many of them were unchanged, except for size, others were embellished with historical notes and figures, legends and the occasional sea monster. Three new maps were added.
There were four editions of Fries' reduced sized re-issue of Waldseemüller's Ptolemy atlas:
1522 Strassburg: 50 woodcut maps, reduced in size, revised by Laurent Fries (Laurentius Frisius) and included the earliest map showing the name ‘America' which is likely to be available to collectors
1525 Strassburg: re-issue of 1522 maps
1535 Lyon: re-issue of 1522 maps, edited by Michael Servetus who was subsequently tried for heresy and burned at the stake in 1553, ostensibly because of derogatory comments in the atlas about the Holy Land – the fact that the notes in question had not even been written by Servetus, but were copied from earlier editions, left his Calvinist persecutors unmoved
1541 Vienne (Dauphiné): re-issue of the Lyon edition - the offensive comments about the Holy Land have been deleted
(Moreland and Bannister)