Leen Helmink Antique Maps
Antique map of Africa by Münster
The item below has been sold, but if you enter your email address we will notify you in case we have another example that is not yet listed or as soon as we receive another example.
Stock number: 18659
Zoom ImageDescription
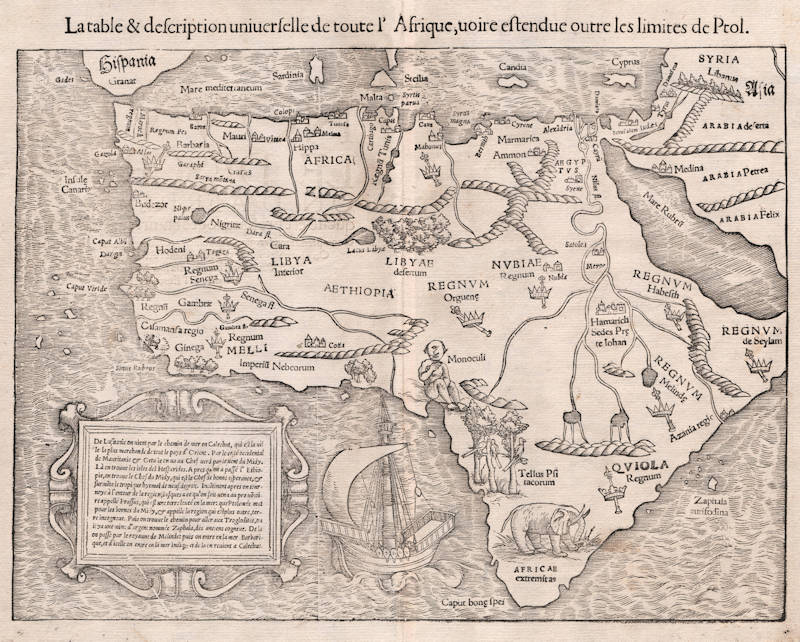
Münster's classical map of the continent. Prester John is located in Ethiopia ('Sedes Prete Iohan').
"This well-known woodblock map is probably as famous for its 'monoculi' (one-eyed man) as for the fact that it is the first map of the continent which collectors can reasonably hope to acquire."
(Jonathan Potter).
"A popular map of Africa is that which appears in the various editions of Münster's Cosmographia. This map, printed from a woodblock, poor in its geographical content, is attractive to collectors, not only on account of pictorial value, being adorned with small figures of a cyclop, elephant, native potentates, etc., but as being the earliest map of Africa that is generally available."
(Ronald Tooley).
"Early woodcut map of the entire continent, the first such work available to collectors. A pictorial work, with cyclops, ship, and an elephant. The Kingdom of Prester John is indicated.
R. V. Tooley comments that 'Munster's map is based partly on Ptolemaic, partly on Portuguese and partly on Arabic sources. Zaphala Aurifodina of Portuguese origin is the supposed region from whence King Solomon imported his gold and silver. Quiloa and Melinda were Arab settlements. It also shows Hamarich, the capital of the famous Christian king, Prester John. The Cape of Good Hope is marked, and the Nile flows into the Mountains of the Moon, south of which the country (the Cape) is said to be uninhabited.
Crowns and sceptres indicate kingdoms; and parrots, elephant and a Cyclops illustrate its western shores, with a fine galleon in full sail to the left of the Cape of Good Hope."
(Suárez).
Sebastian Münster (1489-1552)
Following the various editions of Waldseemüller's maps, the names of three cartographers dominate the sixteenth century: Mercator, Ortelius and Münster, and of these three Münster probably had the widest influence in spreading geographical knowledge throughout Europe in the middle years of the century.
His Cosmographia, issued in 1544, contained not only the latest maps and views of many well-known cities, but included an encyclopaedic amount of detail about the known - and unknown - world and undoubtedly must have been one of the most widely read books of its time, going through nearly forty editions in six languages.
An eminent German mathematician and linguist, Münster became Professor of Hebrew at Heidelberg and later at Basle, where he settled in 1529. In 1528, following his first mapping of Germany, he appealed to German scholars to send him "descriptions, so that all Germany with its villages, towns, trades, etc. may be seen as in a mirror", even going so far as to give instructions on how they should "map" their own localities. The response was far greater than expected and such information was sent by foreigners as well as Germans so that, eventually, he was able to include many up-to-date, if not very accurate, maps in his atlases.
He was the first to provide a separate map of each of the four known Continents and the first separately printed map of England. His maps, printed from woodblocks, are now greatly valued by collectors. His two major works, the Geographia and the Cosmographia were published in Basle by his step-son, Henri Petri, who continued to issue many editions after Münster's death of the plague in 1552.
(Moreland & Bannister).
The remaining modern maps, [...], are all drawn on a plane projection, undergraduated, without scales, and variously oriented with north, south, east or west at the top, "without the excuse of topographical necessity", as Nordenskjöld severely remarks. In spite of these and other cartographic defects, they constitute an important corpus of geographical knowledge and interpretation; Münster was the first atlas-maker to furnish separate maps of the four continents then known; and for England, Scandinavia and southern Germany, eastern Europe and America he brought recent and significant representations into general currency.
(Skelton).
The Cosmographia of Sebastian Münster must rank as the greatest geographical compendium of the period - an immensely detailed work illustrated with woodcut portraits, scenes, town plans and panoramas, and maps. Born in 1488, Münster was a Fransiscan who became Professor of Hebrew at Heidelberg and later at Basle, where he taught Hebrew and, amongst other works, published the first German translation of the Bible from Hebrew. In 1540 his edition of Ptolemy's Geographia was published, followed in 1544 by the Cosmographia Universalis. Together these ran to over 35 editions published mostly in Basle in Latin, German, French and Italian versions. Münster's particular cartographic importance lies in the number of 'new' maps he introduced and, above all, in the innovative, separate mapping of each of the four continents. The map of the Americas is not only the first map to show the Western Hemisphere separately, but is also the first to show North and South America joined together.
(Potter p38).
Sebastian Münster was raised as a Franciscan monk, converted to Lutheranism, taught Hebrew at Heidelberg and Basle, and was proficient in Greek and some Asian tongues. He died of the plague in 1552. First published in 1540, his atlas was the first to contain separate maps of each of the four continents.
(Suárez).
In 1540 Sebastian Münster, who was to become one of the most influential cartographers in the sixteenth century, published his edition of Ptolemy's Geographia with a further section of modern, more up-to-date maps. He included for the first time a set of continental maps, the America was the earliest of any note. Münster studied Hebrew at Heidelberg and was a scholar of geography, writing amongst other works the Polyhistor.
He was one of the first to create space in the woodblock for the insertion of place-names in metal type. The map's inclusion in Münster's Cosmography, first published in 1544, sealed the fate of "America" as the name for the New World. The book proved to be very popular, there being nearly forty editions during the following 100 years.
(Burden).