Leen Helmink Antique Maps & Atlases
www.helmink.com
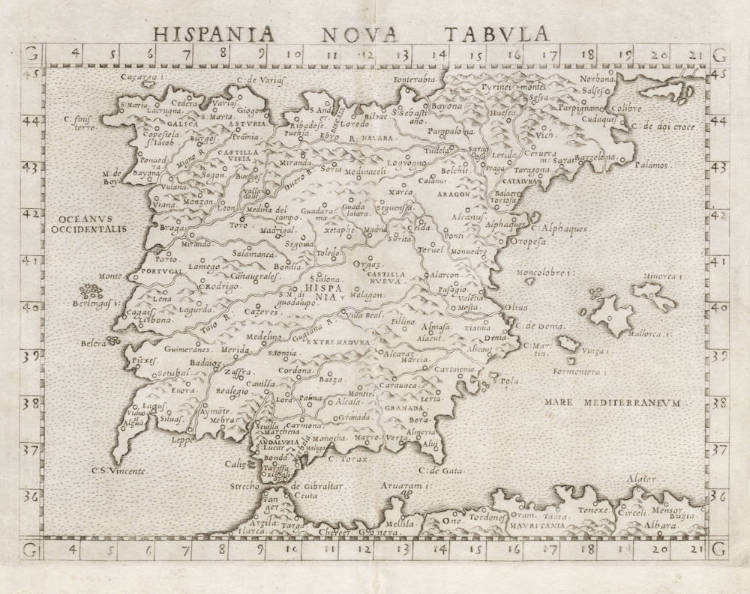
Ruscelli / Gastaldi - Hispania Nova Tabula
Certificate of Authentication
This is to certify that the item illustrated and described below is a genuine and
original antique map or print that was published on or near the given date.
Dr Leendert Helmink, Ph.D.
Cartographer
Girolamo Ruscelli
First Published
Venice, 1561
This edition
1562 first state
Size
17.8 x 24.6 cms
Technique
Copper engraving
Stock number
18877
Condition
excellent
Description
Ruscelli's enlarged version of the 1548 Gastaldi miniature map of Spain and Portugal. A landmark map for the Iberian peninsula.
First state, with the copperplate running off the top edge.
Girolamo Ruscelli (1504-1566)
Girolamo Ruscelli (1504 Viterbo -1566 Venice), an Italian Alchemist, Physician and cartographer, was editor of a revised and expanded Italian edition of Ptolemy's 'Geographia', published as 'La Geografia di Claudio Tolomeo. The newly engraved maps were based, generally, on those compiled by Giacomo Gastaldi for the Venice miniature atlas edition of 1548.
Ruscelli's atlas was issued several times between 1561 and 1599 by the following publishers
- Venice, Vincenzo Valgrisi, 1561
- Venice, Vincenzo Valgrisi, 1562
- Venice, G. Zileti, 1564
- Venice, G. Zileti, 1574
- Venice, Heirs of Melchior Sessa, 1598-99
The Ruscelli and Gastaldi atlases were the most comprehensive atlases produced between Martin Waldseemüller's 'Geographia' of 1513, and Abraham Ortelius 'Theatrum' of 1570. The significance of the Gastaldi and Ruscelli atlases cannot be overestimated. They defined the known geography of the world for decades. These atlases also reintroduced the use of copper engraving into the service of cartography, which was dominated by woodcut printing after several not very succesful attempts to print from copper in the 15th century. The Gastaldi and Ruscelli atlases proved that maps could be beautifully engraved on copper. As it was a harder material than wood, it was harder to engrave but also gave the ability to render much more detail. The Gastaldi and Ruscelli atlases marked a turning point in the history of cartography, from then on the majority of cartographic works used this medium.
"Ruscelli was editor of a revised and expanded edition of Ptolemy's Geographia which was issued in Venice several times between 1561 and the end of the century.
The newly angraved maps were based, generally, on those compiled by Giacomo Gastaldi for the Venice edition of 1548."
(Moreland & Bannister).